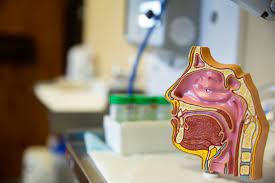
The Ear:
Outer Ear: Housing the auditory canal, linking the
inner and outer ears.
Tympanic Membrane: Serving as a surrogate for the
eardrum.
Middle Ear: Hosting ossicles for sound transmission
and the Eustachian tube for pressure regulation.
Inner Ear: Encompassing the vestibule, semicircular
canals with balancing receptors, and the cochlea housing hearing nerves.
The Nose:
External Nose: Evident on the exterior.
Septum: Providing structural support to the external
nose.
Nasal Passages: Lined with mucus and microscopic
hairs for effective air filtration.
The Throat:
Larynx: Home to vocal cords, influencing breathing
and speech, and serving as a pathway to the trachea.
Epiglottis: Preventing food from entering the
windpipe.
Tonsils and Adenoids: Housing lymph tissue in the
rear of the mouth, contributing to the immune system.
Unique Connection Between the Ear, Nose, and Throat:
The distinctive nature of the interconnection between the ear, nose, and throat lies in their ability to function as a unified system, offering mutual support. The throat facilitates a vital link between the esophagus and lungs, connecting the nose to the mouth and enabling the drainage of fluid from the ears.
This intricate network ensures a simultaneous
connection between the nasal passages and ears. Infections or issues in one
area have the potential to uniquely impact the entire Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT)
system, underscoring the singular nature of their interdependence. Conditions
like post-nasal drip, congestion, edema, and infections can manifest
collectively, reflecting the distinctive and unified nature of the ENT system.
Comments
Post a Comment